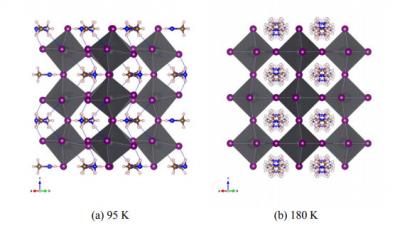
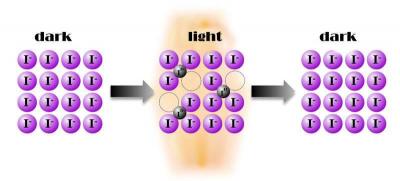
Northwestern and ANL researchers develop a novel perovskite-based nuclear radiation detector
Researchers from Northwestern University and Argonne National Laboratory research team have developed a perovskite-based next-generation device for nuclear radiation detection that could provide a significantly less expensive alternative to the detectors now in commercial use.
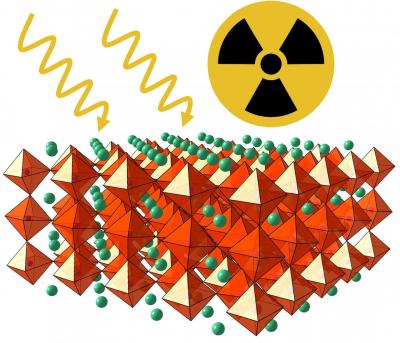
The high-performance material is used in a device that can detect gamma rays, weak signals given off by nuclear materials, and can efficiently identify individual radioactive isotopes. The new material also has the advantage of inexpensive production. Potential uses for the new device include more widespread detectors for nuclear weapons and materials as well as applications in biomedical imaging, astronomy and spectroscopy.