 Oxford Photovoltaics Limited (Oxford PV) was founded in 2010 as a spin-out from the University of Oxford to commercialize a new technology for thin-film solar cells. It was amongst the first in the world to recognize the potential of perovskites to act as a low-cost, highly efficient solar cell absorber material to convert sunlight into electricity.
Oxford Photovoltaics Limited (Oxford PV) was founded in 2010 as a spin-out from the University of Oxford to commercialize a new technology for thin-film solar cells. It was amongst the first in the world to recognize the potential of perovskites to act as a low-cost, highly efficient solar cell absorber material to convert sunlight into electricity.
Oxford PV is developing and commercializing thin-film perovskite solar cells, which can be printed directly onto silicon solar cells, CIGS solar cells or glass. Pioneering work developing perovskite thin-film solar cells has delivered a route to boosting the efficiency of current commercial cells; using a high efficiency coating in a multi-junction or “tandem†cell architecture. In addition, printing perovskites directly onto glass has led to a semi-transparent coating ideal for BIPV applications and, once integrated into the glazing units of a building, the technology is capable of providing a significant percentage of the building’s electrical energy requirements directly from sunlight.
By employing well known and well understood printing processes, focused on inexpensive and abundant raw materials, Oxford PV has developed a highly cost effective technology.
The company has exclusively licensed the rapidly growing portfolio of fundamental intellectual property developed by its academic team.
Oxford PV has acquired the former thin-film production site of Bosch Solar in Germany, to establish a fab with pilot-scale capacity for perovskite wafers. To that end, the Company also received funding of €15 million form the European Investment Bank (EIB), to support the commercialization of its perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cell technology. In June 2018, Oxford PV reported a new perovskite tandem solar cell record, certified by Fraunhofer ISE at a conversion efficiency of 27.3%. Oxford PV’s latest record for a 1 cm2 perovskite-silicon tandem solar, reportedly exceeds the former 26.7% efficiency world record for a single-junction silicon solar cell.
Unit 7-8 Oxford Industrial Park Mead Road
Oxford
OX5 1QU
United Kingdom
The latest Oxford PV news:
Oxford PV and Fraunhofer ISE announce full-sized tandem PV module with 25% efficiency
A research team from the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE has reported a PV module using perovskite silicon tandem solar cells from Oxford PV with an efficiency of 25% and an out-put of 421 watts on an area of 1.68 square meters, stating it is a record efficiency for a silicon perovskite tandem solar module in industrial format.
For the manufacturing process, the researchers used equipment at Fraunhofer ISE's Module-TEC that is already used in mass production and optimized the processes for the tandem technology.
Researchers examine shingling as an interconnection method for perovskite-silicon tandems
A group of scientists from Germany's Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (Fraunhofer ISE), with support from Oxford PV Germany, have examined shingling as an interconnection method for perovskite-silicon tandem (PVST) cells.
Full-format perovskite-silicon tandem shingle modules produced at Fraunhofer ISE in collaboration with Oxford PV. Image from Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells.
The scientists explained that the combination of PVST cells with shingling allows boosting the module efficiency even further due to the increase of the photoactive area through the absence of cell gaps. They went on to say that shingling suits the temperature limitations of the PVST cells since the main factor for the choice of the processing temperature is the curing conditions of the electrically conductive adhesive.
Oxford PV's perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cells used in the Bridgestone World Solar Challenge
Oxford PV has announced that its perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cells will be deployed for the first time on the race car of the Top Dutch Solar Racing team for the upcoming Bridgestone World Solar Challenge.
Taking place between the 22nd and 29th of October 2023, the competition brings some of the world’s greatest scientific and engineering talent to Australia to travel 3,000 kilometers in a vehicle powered only by the energy of the sun. University-affiliated teams push the limits of technological innovation and travel the outback in solar-powered vehicles that they have designed, engineered and ultimately built themselves.
Researches develop low-temperature processes to reduce silver use in tandem perovskite-silicon solar cells
Researchers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (Fraunhofer ISE) and Oxford PV Germany have developed low temperature manufacturing processes for perovskite silicon tandem cells and heterojunction solar cells. The novel techniques are reportedly able to reduce silver consumption and avoid lead-containing soldering materials.
The scientists developed two different processes: front-side metallization at very low temperatures for full-size perovskite silicon tandem solar cells; and the interconnection to high-efficiency full-format demonstrator modules with an output power of more than 400 W.
Oxford PV announces new efficiency record
Oxford PV has announced 'a new world record for the efficiency of a commercial-sized solar cell'. The efficiency record was achieved on a commercial-sized ‘M4’ (258.15 cm2) solar cell. The cell is a 2T device made by depositing a perovskite thin-film cell onto a conventional silicon heterojunction cell.
The record-breaking solar cell converted 28.6% of the sun’s energy into electricity, as independently certified by Fraunhofer ISE. The solar cell was produced at Oxford PV’s integrated production line in Brandenburg an der Havel, Germany. The factory has commenced initial production of the company’s tandem solar cells for integration by solar module manufacturing partners and is ramping up to higher volumes. The site, operational since 2017, houses the world’s first volume manufacturing line for perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cells.
"Katana" project to establish reliable measuring system for tandem solar cells
To pave the way for the industrial implementation of efficient perovskite-silicon PV modules, a reliable measuring system for tandem solar cells and modules must be established. Only then can objective comparisons between different cells and modules take place. In contrast to conventional silicon PV modules, however, the calibration is considerably more challenging.
A project consortium, led by the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE, is therefore developing methods for characterizing perovskite-based tandem modules in the "Katana" project, funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate BMWK. The solar simulator specially built for this purpose by the company Wavelabs Solar Metrology Systems GmbH is now in use in the CalLab PV Modules of the research institute.
New project will utilize quantum computing to advance perovskite PV materials
A UK-based quantum software company called Phasecraft will lead a project modelling new perovskite-silicon materials for solar photovoltaics. The project, in collaboration with Oxford PV and scientists at University College London (UCL), is aimed to support the development of quantum computing to simulate “currently intractable problems” in PV materials modelling, according to a recent statement.
Not many details were given regarding the new project, which received an award from UK Research and Innovation’s Commercializing Quantum Technologies Challenge. It was, however, said that it will set out to develop a modelling capability that is tailored to the real-world needs of the PV industry.
Researchers examine the environmental performance of perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cells
A team of scientists from Technische Universität Berlin, Oxford PV Germany, German Philipps-Universität Marburg, Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and Oxford PV UK has, for the first time, assessed the environmental performance of industrially produced perovskite-on-silicon PV modules. Understanding the environmental impact of solar PV modules across their entire lifecycle is essential for the design of more sustainable solar energy systems. However, lifecycle assessment of perovskite-on-silicon PV modules has so far relied heavily on data from laboratory and test facilities rather than manufacturers.
The researchers conducted a comprehensive lifecycle assessment of a perovskite-on-silicon module across a number of categories including global warming potential, water consumption, human and marine toxicity, and metals usage. They assessed the materials and energy input for a module’s ‘cradle to gate’ lifecycle, covering all materials and energy input for wafer production, manufacture of the perovskite cell, and module production. The researchers then weighed up the environmental impact of the tandem module against the electricity generated over its lifetime.
When will perovskite solar panels hit the market?
Perovskite solar panels have been under intensive R&D, and it seems as if commercial production is right around the corner. Some pilot-scale production lines are already functional, and companies are now ramping up production of perovskite panels, using various technologies.
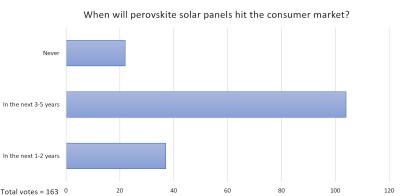
UK-based Oxford PV, for example, recently announced that it has completed the build-out of its 100 MW manufacturing site in Germany, and it is on track to start full production in 2022. China's Microquanta Semiconductor perovskite panel factory is reportedly also nearing production (which should have started late 2020, but updates have not been available since), and another China-based company, GCL, has raised around $15 million USD to expand its pilot-scale production factory to mass production (100 MW).
Oxford PV explains the benefits of pairing perovskites with silicon
Scientists from Oxford PV have recently published a study describing how pairing metal halide perovskites with conventional silicon leads to a more powerful solar cell that overcomes the 26% practical efficiency limit of using silicon cells alone.
'We identified perovskites as the perfect partner for a tandem system with silicon,' commented author Laura Miranda Pérez.
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page





