Perovskite Quantum Dots (PQDs)
Perovskites are materials that share a crystal structure similar to the mineral called perovskite, which consists of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3).

Depending on which atoms/molecules are used in the structure, perovskites can possess an impressive array of interesting properties including superconductivity, ferroelectricity, charge ordering, spin dependent transport and much more. Perovskites therefore hold exciting opportunities for physicists, chemists and material scientists.
Quantum dots (QDs), sometimes referred to as semiconducting nanocrystals (NCs), are miniscule particles of a semiconducting material with diameters in the range of 2-10 nanometers (10-50 atoms). Quantum dots have properties labeled as intermediate between bulk semiconductors and discrete atoms or molecules. Their optoelectronic properties change as a function of both size and shape. QDs demonstrate optical and electronic properties different from those of larger particles. In fact, QDs tend to exhibit quantum size effects in their optical and electronic properties, like tunable and efficient photoluminescence (PL), with narrow emission and photochemical stability. This is why QDs have been incorporated as active elements in a wide variety of devices and applications, some of which are already commercially available, such as QD-based displays.
Perovskite quantum dots (PQDs) are a class of quantum dots based on perovskite materials. While these are relatively new, they have already been shown to have properties matching or surpassing those of the metal chalcogenide QDs: they are more tolerant to defects and have excellent photoluminescence quantum yields and high colour purity. Such attractive properties are extremely suited for electronic and optoelectronic applications and so perovskite quantum dots have significant potential for real world applications, some of which are already emerging, including LED displays and quantum dot solar cells.
Researchers report annealing-free flexible perovskite quantum dot solar cells that use UV-sintered Ga-doped SnO2 electron transport layers
Researchers from Hanyang University, Nankai University and Kookmin University have developed a room-temperature-processed tin oxide (SnO2) ETL preparation method for flexible perovskite quantum dots (PQD) solar cells. Low-temperature ETL deposition methods are especially desirable for fabricating flexible solar cells on polymer substrates.
The process involves synthesizing highly crystalline SnO2 nanocrystals stabilized with organic ligands, spin-coating their dispersion, followed by UV irradiation. The energy level of SnO2 is controlled by doping gallium ions to reduce the energy level mismatch with the PQD.
Perovskite-Info launches a new edition of its Perovskite for Displays Market Report
Perovskite-Info is proud to announce an update to our Perovskite for the Display Industry Market Report. This market report, brought to you by the world's leading perovskite and OLED industry experts, is a comprehensive guide to next-generation perovskite-based solutions for the display industry that enable efficient, low cost and high-quality display devices. The report is now updated to February 2024, with all the latest commercial and research activity. This was a major version, with over 15 updates, new companies and new technologies covered.
Reading this report, you'll learn all about:
- Perovskite materials and their properties
- Perovskite applications in the display industry
- Perovskite QDs for color conversion
- Prominent perovskite display related research activities
The report also provides a list of perovskite display companies, datasheets and brochures of pQD film solutions, an introduction to perovskite materials and processes, an introduction to emerging display technologies and more.
Researchers develop strategy that enables world's most efficient quantum dot solar cell
Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) researchers have developed solar cells using narrow bandgap organic cation-based perovskite-based quantum dots (PQDs) and demonstrated substantially higher efficiency compared with their inorganic counterparts.
The team stressed that research to this point has predominantly focused on inorganic cation PQDs despite the fact that organic cation PQDs have more favorable bandgaps. However, the recent study unveiled a novel ligand exchange technique, that enables the synthesis of organic cation-based PQDs, ensuring exceptional stability while suppressing internal defects in the photoactive layer of solar cells.
Researchers manage to make perovskite quantum dots even brighter
A team of researchers, led by Maksym Kovalenko at ETH Zurich and Empa, working in collaboration with scientists from the U.S. and Ukraine, recently demonstrated how the promising properties of perovskite quantum dots can be improved further. They used chemical methods for surface treatment and quantum mechanical effects that had never before been observed in perovskite quantum dots.
Perovskite quantum dots can be mixed with liquids to form a dispersion, which makes them easy to process. Moreover, their special optical properties make them shine more brightly than many other quantum dots. They can also be produced more cheaply, which makes them interesting for applications in displays, for instance. On top of all this, the newly developed phospholipid molecules create a protective layer around the perovskite nanocrystal and make it possible to disperse it in non-aqueous solutions. They also ensure that the quantum dot emits photons more continuously.
Avantama and Scrona make strides in perovskite quantum dots processing
Swiss additive manufacturing startup Scrona and Avantama, developer and manufacturer of high-tech materials for electronics, have jointly announced that they have successfully processed high-performance perovskite quantum dot (QD) ink using Scrona's electrohydrodynamic (EHD) inkjet printing.
This collaboration combines the benefits of the inkjet process with high-patterning resolution to drive a new generation of efficient and cost effective MicroLED displays, while also increasing color purity and brightness, and improving overall pixel production tact time.
Researchers boost signal amplification in perovskite nanosheets
Researchers at Pusan National University and the University of Oxford have made an advanced in the field of perovskite nanosheets as promising new laser materials. The team overcame the inherent limitations of CsPbBr quantum dots using perovskite nanosheets, which provide enhanced light amplification abilities.
The researchers introduced an innovative waveguide pattern, which increased the gain and thermal stability of the perovskite nanosheets. This pattern improved the optical confinement and heat dissipation, offering a solution to the limitations previously faced with quantum dots. The research team also pioneered a new ‘gain analysis’ method known as the ‘gain contour’. This novel technique provides a more in-depth understanding of gain saturation across various spectrum energies and optical stripe lengths.
Helio Display Materials to move perovskite-based display materials to pilot-scale production
Helio Display Materials has announced it will be moving its perovskite-based display materials (that were jointly invented within Cambridge and Oxford Universities) to pilot-scale production.
The materials generate light of the desired color by converting light rather than filtering it which provides power savings of up to 40% and a step change improvement in color gamut. With perovskites, the wavelength of emitted light can be tuned by chemical composition. This contrasts with quantum dots which rely on quantum confinement in identically sized nanometer scale particles. Color by composition massively simplifies the manufacturing process for perovskites vs. quantum dots and allows the use of standard chemical industry processes and equipment.
Researchers use a self-driving fluidic lab to quickly identify best-in-class perovskite QDs
Researchers at North Carolina State University, Brown University and University at Buffalo have developed an autonomous system that can identify how to synthesize “best-in-class” materials for specific applications in hours or days.
The new system, called SmartDope, was developed to address a persistent challenge regarding enhancing properties of perovskite quantum dots via “doping.”
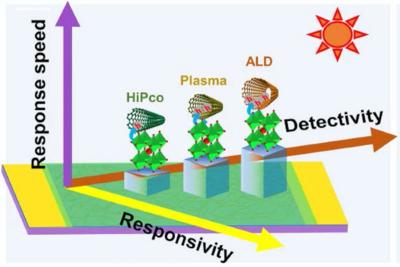
Researchers explore how carbon nanotube diameter can influence the performance of photodetector heterojunctions
Researchers from China's Hebei University of Technology and Chinese Academy of Sciences have found that increasing the diameter of single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) in SWCNT/perovskite QD heterojunctions can improve the optoelectronic performance of the heterojunction between the two materials.
The team systematically tested the performance effects of varying diameters of SWCNTs, a single layer of carbon atoms that form a hexagonal lattice rolled into a seamless cylinder, with different band gaps, or the amount of energy required for an electron to conduct electric current, in heterojunction films with perovskite QDs. Their study indicated that increasing the diameter of SWCNTs improved the responsivity, detectivity and response time of this type of heterojunction film. This effect may be mediated by the enhanced separation and transport of photogenerated excitons, an energy-carrying, neutrally charged electron that combines with a positive electron hole, in the film.
TCI's molecular dopants boost organic electronics
TCI has launched a range of molecular dopants that can significantly increase the charge carrier density and modify the energy levels in organic electronics devices. Molecular dopants offer a versatile platform to tune the optoelectrical and electrical properties of organic semiconductors to application-specific demands, allowing advantages like increasing the electrical conductivity and mobility by orders of magnitude and improving contact properties in various electronic and optoelectronic devices.
TCI's p-type and n-type dopants can be applied to various organic electronics devices, such as: carrier transport layers of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), organic photovoltaics (OPVs), perovskite solar cells (PSCs), and perovskite quantum dot LEDs, as well as active layers of organic field-effect transistors (OFETs), OPVs, and thermoelectric devices in the field of organic electronics research.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 2
- Next page