Solliance team breaks 30% efficiency barrier
Solliance partners TNO, TU Eindhoven, imec and TU Delft have joined forces to further push the conversion efficiency of tandem solar cells to beyond the limits of today’s commercial PV modules. They have achieved an extraordinary feat: the first time that four-terminal perovskite/silicon tandem devices with certified top cell passed the barrier of 30%.
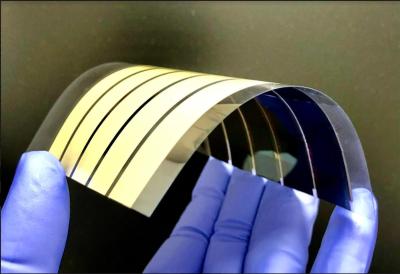
Bottom silicon solar cell and top perovskite solar cell with transparent contacts. Photo credit: Niels van Loon
Such high efficiency enables more power per square meters and less cost per kWh. The result was presented during the 8th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion (WCPEC-8) in Milan and has been achieved by combining perovskite solar cell tech with conventional silicon solar cell technologies. The perovskite cell that features transparent contacts and is part of the tandem stack has been independently certified.