This is a sponsored post by MBRAUN
The potential of perovskites
Over the past decade, perovskites solar cells have attracted tremendous interest from the academic community, becoming a leading photovoltaic trend. Advances in the fundamental understanding of perovskites’ chemical and physical processes made them an attractive class of material for many researchers. In parallel, engineering developments on the architecture and fabrication methods of perovskite-based solar cells are becoming increasingly interesting for the PV industry.
Processing of perovskites
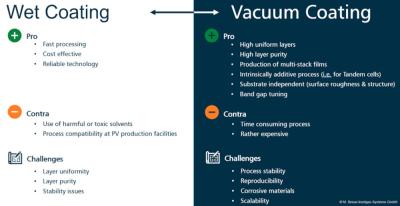
In general, three main types of perovskites processes can be distinguished – the fully vacuum-processed, the fully ambient processed and the hybrid type. For each process, MBRAUN can offer dedicated equipment solutions which will be showed in outline in the following paragraphs.
On one hand vacuum-based methods convince due to high-quality thin films, leading to the best device performance but are but are also characterized by comparatively high investment and operating costs. On the other hand, solution-processing techniques, like spin coating or slot-die coating also produce good-quality layers but excel at significantly lower investment and operation costs.
Comparison of wet and vacuum coating